Open data: A look at global climate conditions from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Please close your eyes and imagine a world in which data that describes most human activities in a nation is freely available, reliable, and commonly used by businesses, consumers, journalists, and local, national, and international governments and organizations. This data comes raw and processed from people, sensors, computers, networks, community groups, businesses, blogs and media outlets, political parties, courts, police and fire departments, airplanes, trains, satellites, deep sea and space stations. It flows real-time and batch in every conceivable structured and unstructured format, and every year its velocity, variety, and volume contribute 5-10% of additional GDP growth by enabling new things to happen that could never even be imagined without access to this vital natural resource: knowledge.
The world I describe above was first imagined by the U.S. Government in 2009, when Data.Gov was created. And since then, hundreds of cities, states, and nations around the world have embraced the concept of open data and open government by publishing millions of data sets of dubious quality that few people are aware of and hardly anyone really uses.
Why?
Why is there so much data of questionable quality that less than 1% of the population of the world is using when there could be tremendous demand for extremely valuable data that could make a huge difference in everyone’s lives?
Why aren’t cities, states, and nations publishing data about all their procurement contracts, road construction projects, environmental impact surveys, aggregate weekly business demand, daily housing starts, monthly company earnings reports?
Money.
To publish more data you need more money. And historically, data management is a woefully underfunded organizational activity.
Not just in government. Everywhere.
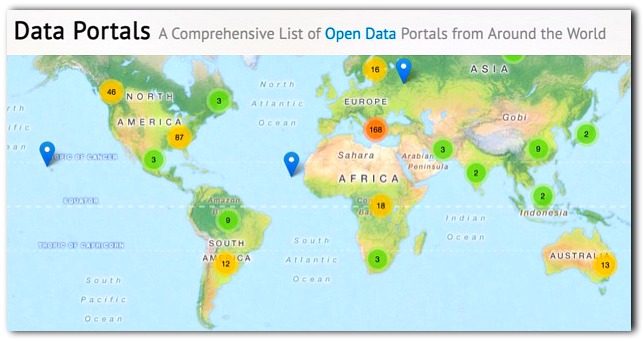 In most cities and countries the number of people in a government working on open data is normally one or two. And in many countries it is international aid organizations who fund the open data programs. Data.Gov in the United States is run by four people. It has satellite maps that could provide the world’s first comprehensive inventory of global agricultural production for every crop produced by every country. That’s data that many subsistence farming nations don’t even have about their own production. With that data we could end world hunger in a few years and ensure agricultural security in the face of certain climate change over the next decade. Why isn’t it being done?
In most cities and countries the number of people in a government working on open data is normally one or two. And in many countries it is international aid organizations who fund the open data programs. Data.Gov in the United States is run by four people. It has satellite maps that could provide the world’s first comprehensive inventory of global agricultural production for every crop produced by every country. That’s data that many subsistence farming nations don’t even have about their own production. With that data we could end world hunger in a few years and ensure agricultural security in the face of certain climate change over the next decade. Why isn’t it being done?
No money.
Someone somewhere wants a pre-study for a study to build a business case for data to be found, collected, curated, and published to specific audiences for specific purposes to measure, with KPI’s (key performance indicators), exactly how the business case for the investment to hire the resources and build the solution to provide the data should be documented so the committee can reject it due to budget cuts.
Open government and open data are unfunded mandates that could be/should be producing really profound changes in how government institutions are organized, how information is shared between government departments and other governments, how public and private partnerships are created, how new businesses are started, how existing ones develop new products and markets, how communities solve problems, how journalists uncover hidden truths, and how the benefits of governance itself is measured.
But this isn’t being done today and the first step to helping change the world is to study what’s working and what’s not. I see a lot of great organizations discussing parts of the issues in closed communities, councils, and companies. But I think open data and open governance affect everyone and everyone should be included by default in the possibility to contribute to the conversation.
I am not an expert on all the issues, but I do think there are experts who want to participate. The IBM Open Governance Council has been created to enlist experts the world over to participate in a public forum where tough challenges are explored in a fully transparent and open environment that ANYONE can join.
Here are some questions we can start exploring:
- How Open changes public and private Governance — the state within states must open up?
- How data management can strengthen governing institutions and restore public trust?
- How to achieve a hundredfold increase in data management investment?
- How to address the need for more and better data science skills?
- How to ensure all organizations have and use common standards in records retention, metadata, publication, and archiving?
- How to make sure broadband bandwidth keeps pace with cloud data demands over the next decade?
- How to include people in policy decisions?
- How to open up procurement transactions and eliminate corruption?
- How to change organizational behavior sustainably?
Those are some questions I have been thinking about that could be explored. But it’s an open council, with open and fully transparent rules, and I will encourage members to bring their own questions, challenges, solutions, and ideas.
I think we can make a difference. We will self-organize meetups, meetings, conferences, and calls as needed. And we will, if needed, create, endorse, promote, and recommend ideas, standards, pilots, and projects.
There is only one requirement to join. You have to state your agreement with this Open Governance Declaration.
Join us and help make Data the Open, Free and Ubiquitous Natural Resource that Improves Governance, Business, Science, and Human Progress.
P.S. It is only “IBM” because I work for IBM and my company cares about these issues and we think it’s important to step up and make a difference.
 Steven Adler (@DataGov) is chief information strategist for IBM. He is an expert in data science and an innovator who has developed billion-dollar-revenue businesses in the areas of data governance, enterprise privacy architectures, and Internet insurance. He has advised governments and large NGOs on open government data, data standards, privacy, regulation, and systemic risk.
Steven Adler (@DataGov) is chief information strategist for IBM. He is an expert in data science and an innovator who has developed billion-dollar-revenue businesses in the areas of data governance, enterprise privacy architectures, and Internet insurance. He has advised governments and large NGOs on open government data, data standards, privacy, regulation, and systemic risk.

Open Data from Space to Solve Drought in California – Join USDA Under Secretary Dr. Catherine Woteki as we explore Open Data, Agriculture, and Climate Change in California. We want to explore how Open Data can benefit businesses, engage citizens, and shape public policy and Open Governance.
http://www.meetup.com/The-IBM-Open-Governance-…/…/221756087/